- Abdominal Hernia Surgery in Dombivli
- Anal Fissure Laser Surgery in Dombivli
- Appendix Treatment in Dombivli
- Bariatric Surgery in Dombivli
- Best Laparoscopic Surgeon in Dombivli
- Blogs
- Cases Operated
- Colorectal Cancer Treatment in Dombivli
- Contact us
- Custom
- Dr Rahul Mahadar
- Dr. Dhanashree Mahadar
- Endoscopy Clinic in Dombivli
- Ent Surgeon in Dombivli
- Gall Bladder Cancer Surgery in Dombivli
- Gallbladder Stone Treatment in Dombivli
- Gastrointestinal Surgeon in Dombivli
- Hernia Surgeon in Dombivli
- Home
- How to Choose the Right Gastroenterologist Near You
- Laser Fistula Surgery in Dombivli
- Laser Piles Surgeon in Dombivli
- Pancreatic Cancer Treatment in Dombivli
- rahul mahadar-1
- Services
- Specialities
- Stomach Cancer Treatment in Dombivli
- Testimonials
- Video
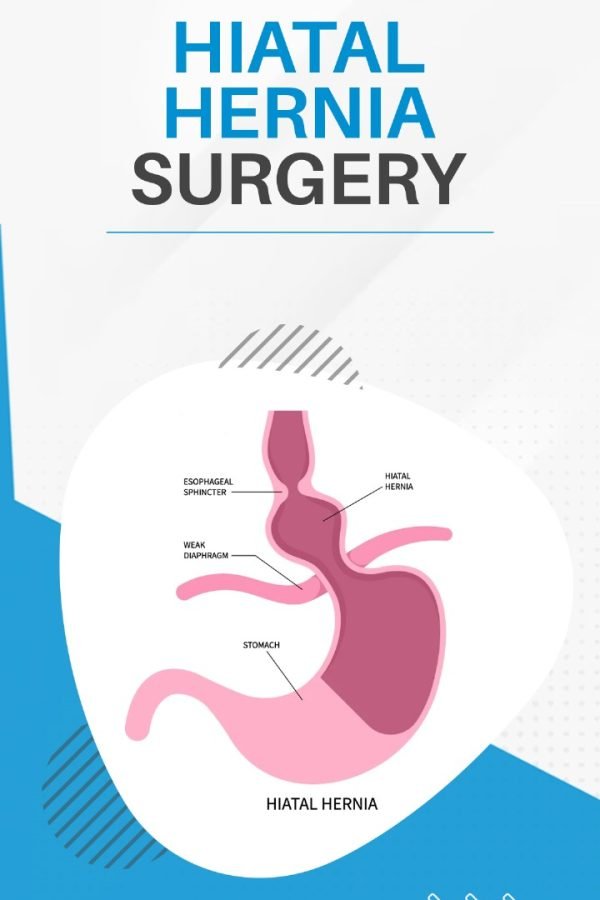

Hiatal Hernia Surgery
Hiatal Hernia is a medical condition where a portion of the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. The diaphragm is the muscle that separates the abdomen from the chest. The opening in the diaphragm through which the esophagus passes is called the hiatus. When the stomach bulges through this opening, it results in a hiatal hernia.
There are two main types of hiatal hernias-
- Sliding Hiatal Hernia: This is the more common type, where the junction of the esophagus and stomach, known as the gastroesophageal junction, and a portion of the stomach slide up into the chest through the hiatus. This type of hernia may not cause symptoms and often goes unnoticed unless detected during tests for other conditions.
- Paraesophageal Hiatal Hernia: In this less common type, the gastroesophageal junction remains in its normal position, but a portion of the stomach pushes through the hiatus and lies alongside the esophagus. This type of hernia can cause more severe symptoms and complications, such as obstruction or strangulation of the stomach.
Why Surgery is Needed for Hiatal Hernia?
While many people with hiatal hernias do not require surgery, those with significant symptoms or complications may benefit from surgical intervention. Surgery for hiatal hernia may be considered if:
- Symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, chest pain, difficulty swallowing, or respiratory issues are not adequately controlled with medications or lifestyle changes.
- There are complications associated with the hiatal hernia, such as bleeding, strangulation, or obstruction of the stomach.
- The hernia is large and causing significant discomfort or interfering with normal activities.
Types of Surgery for Hiatal Hernia
- Nissen Fundoplication: This is the most common type of surgery for hiatal hernia. During a Nissen fundoplication, the surgeon wraps the upper part of the stomach (the fundus) around the lower esophagus to reinforce the lower esophageal sphincter and prevent reflux. This procedure can be performed either through open surgery or laparoscopically (minimally invasive).
- Laparoscopic Hiatal Hernia Repair: In this minimally invasive approach, small incisions are made in the abdomen through which a laparoscope and surgical instruments are inserted. The hernia is repaired by pulling the stomach back into the abdominal cavity and closing the hiatus with sutures or mesh.
- Toupet Fundoplication: Similar to Nissen fundoplication, Toupet fundoplication involves wrapping the stomach around the esophagus. However, in this procedure, the wrap is only partial, leaving the front of the stomach uncovered. This approach may be preferred in some cases to reduce the risk of postoperative side effects such as difficulty swallowing (dysphagia).
Benefits of Surgery for Hiatal Hernia
- Relief of Symptoms: Surgery can provide long-term relief from symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, chest pain, and difficulty swallowing that are not adequately controlled with medications.
- Prevention of Complications: Surgery can prevent complications associated with hiatal hernia, such as esophageal stricture, Barrett’s esophagus, and respiratory problems caused by aspiration of stomach contents.
- Improved Quality of Life: By alleviating symptoms and reducing the risk of complications, surgery can significantly improve a person’s quality of life, allowing them to eat more comfortably and engage in activities without discomfort or restrictions.
- Minimally Invasive Approach: Many surgical techniques for hiatal hernia repair can be performed using minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques, resulting in smaller incisions, less pain, faster recovery, and shorter hospital stays compared to traditional open surgery.
- Long-term Results: Properly performed surgical repair of a hiatal hernia can provide long-term relief, reducing the need for ongoing medication and lifestyle modifications to manage symptoms.
Surgery for hiatal hernia may be recommended for individuals with significant symptoms or complications that do not respond to conservative treatments. Various surgical techniques are available, each with its own benefits and considerations, and the choice of procedure depends on the individual’s specific condition and the surgeon’s expertise. Overall, surgery can offer significant benefits in terms of symptom relief, prevention of complications, and improved quality of life for patients with hiatal hernia.

